Astronomers used Webb’s Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam) to observe the protostar, which is hidden from view and is a way for astronomers to study our Sun.

The protostar within the dark cloud L1527, shown in this image from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam), is embedded within a cloud of material feeding its growth. (Photo: Nasa)
In Short
- James Webb Telescope is located 15,00,000 kilometers away from Earth
- Astronomers used Webb’s Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam) to observe protostar
- The dark cloud L1527 is just 1,00,000 years old
By India Today Web Desk: Hanging in the vacuum of space about 15,00,000 kilometers away from Earth, the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has looked at the protostar within the dark cloud L1527 unraveling secrets of new stars. The observatory peeked into clouds within the Taurus star-forming region in infrared light.
Astronomers used Webb’s Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam) to observe the protostar, which is hidden from view within the “neck” of the hourglass shape. The image shows a dark line across the middle of the neck as light from the protostar leaks above and below this disk, illuminating cavities within the surrounding gas and dust.
ADVERTISEMENT
Nasa releasing the image said that the clouds, coloured blue and orange, outline cavities created as material shoots away from the protostar and collides with surrounding matter. The colors themselves are due to layers of dust between Webb and the clouds. The thicker the layer of dust, the less blue light is able to escape, creating pockets of orange.

“Webb also reveals filaments of molecular hydrogen that have been shocked as the protostar ejects material away from it. Shocks and turbulence inhibit the formation of new stars, which would otherwise form all throughout the cloud. As a result, the protostar dominates the space, taking much of the material for itself,” Nasa said.
Recent Posts
- Astronomers detect first direct image of black hole expelling a powerful jet
- WhatsApp rolling out ‘reply with message’ feature within call notifications
- Multi-Device Pairing May Be Arriving for Apple Watch this Year
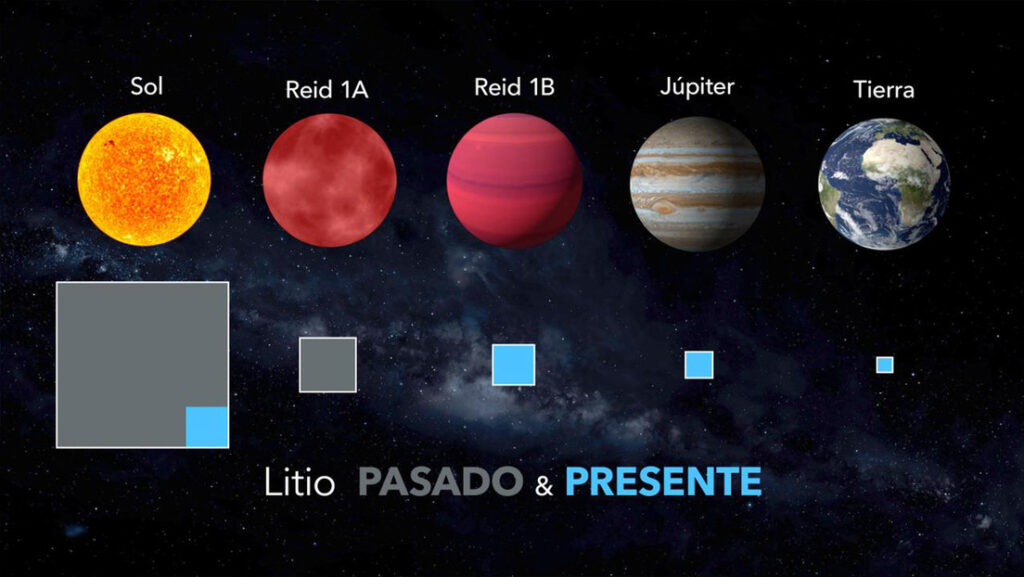
- Artificial Intelligence Discovers Hidden Giant, a Planet 5 Times Larger Than Jupiter
- Google CEO Sundar Pichai Talks Bard & The Future Of Search
Recent Comments

Astronomers detect first direct image of black hole expelling a powerful jet
Artificial Intelligence Discovers Hidden Giant, a Planet 5 Times Larger Than Jupiter

Scientists explain melting of Antarctic ice sheet dating back 9,000 years

An Unexpected Discovery: Hubble, ESA's Gaia Spot Double Quasar That Existed Over 10 Billion Years Ago

Astronomers detect first direct image of black hole expelling a powerful jet

WhatsApp rolling out ‘reply with message’ feature within call notifications

Multi-Device Pairing May Be Arriving for Apple Watch this Year


