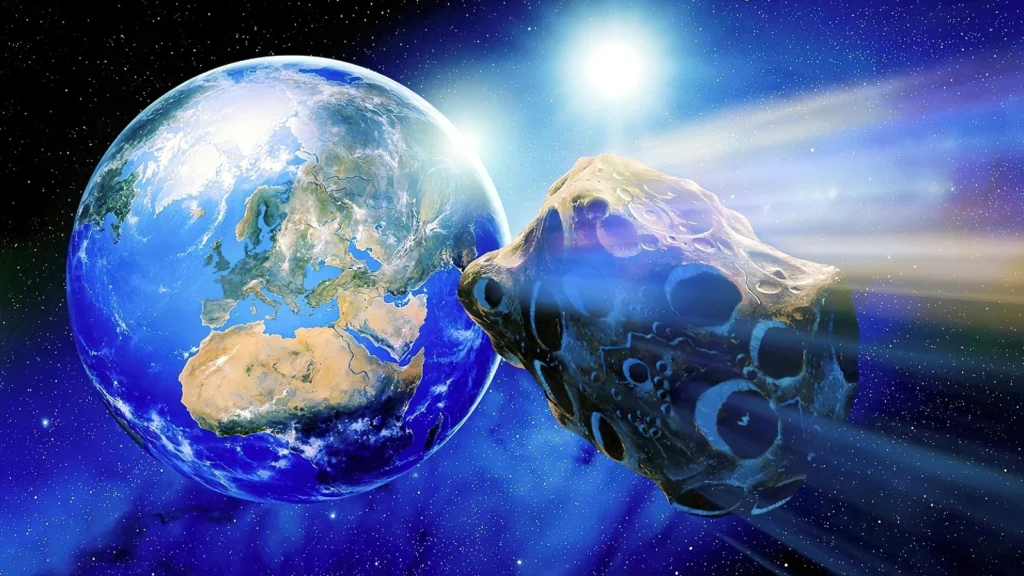
Giant Asteroid 2008 RW to pass Earth on September 13 at a distance of 6.7 million kilometres with a speed of 10 kilometres per second.
In recent weeks, space rocks have been making frequent close passes at earth lately and NASA has been keeping a track of them in order to protect earth from collision. Though they aren’t supposed to pose any threat to our planet, many of them are still classified into potentially dangerous asteroids due to their close approach to earth. As per a report by NASA, an asteroid dubbed as Asteroid 2008 RW as big as 300 feet will reportedly fly past Earth on September 13, at 01:30 at a distance of 6.7 million kilometres with a speed of 10 kilometres per second.
The Tech Behind Asteroid Hunting
There is a huge amount of technology involved in the process of hunting asteroids. So how are NEOs characterised? NASA says, “NEOs are characterized by using optical and radio telescopes to determine their size, shape, rotation, and physical composition. Some of the most detailed characterization data is obtained for NEOs that approach Earth close enough to be observed with planetary radar, performed by radio telescopes at NASA’s Deep Space Network and the National Science Foundation’s Arecibo Observatory in Puerto Rico.”
As shared by Sky.org, this near-Earth object belongs to the Apollo group and is currently 56.02 million kilometres, equivalent to 0.37 astronomical units. It takes 3 minutes and 6 seconds for light to travel from the asteroid 2008 RW to us.
The asteroid was detected on September 02, 2008. The space rock takes 1023 days to complete one orbit around the Sun. Its orbit’s farthest point from the Sun is 456 million kilometres, and the nearest point is 139 million kilometres. It will make its next close pass to earth on September 11, 2036 from 6.9 million kilometres away. However, it doesn’t pose any threat to our planet if it stays on this path and does not diverge from it in any way towards earth.
How are asteroids classified into near-Earth objects?
A space rock that comes within the distance of 30 million miles from Earth is classified as a “near-Earth object” by NASA and any near-earth objects that come within around 4.65 million miles fall into potentially hazardous asteroids category. However, the asteroid “2022 PJ1”, is not classified as a “potentially hazardous object” as its size is estimated in the range from 14 meters to 32 meters.
Do you know?
Asteroids are small, rocky objects leftover from the solar system’s formation around some 4.5 billion years ago. They orbit the sun and mostly reside in the between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter, also known as asteroid belt. They are made of different kinds of rocks, and hence, no two asteroids are alike.
Recent Posts
- Astronomers detect first direct image of black hole expelling a powerful jet
- WhatsApp rolling out ‘reply with message’ feature within call notifications
- Multi-Device Pairing May Be Arriving for Apple Watch this Year
- Artificial Intelligence Discovers Hidden Giant, a Planet 5 Times Larger Than Jupiter
- Google CEO Sundar Pichai Talks Bard & The Future Of Search
Recent Comments

Astronomers detect first direct image of black hole expelling a powerful jet
Artificial Intelligence Discovers Hidden Giant, a Planet 5 Times Larger Than Jupiter

Scientists explain melting of Antarctic ice sheet dating back 9,000 years

An Unexpected Discovery: Hubble, ESA's Gaia Spot Double Quasar That Existed Over 10 Billion Years Ago

Astronomers detect first direct image of black hole expelling a powerful jet

WhatsApp rolling out ‘reply with message’ feature within call notifications

Multi-Device Pairing May Be Arriving for Apple Watch this Year


